
U Tube Manometer II Construction ii Working II Equation YouTube
That is U-tube principle is not suitable to locate multiple gas-leak points. U-tube principle takes pressure balance position as the location of leakage point (Wu et al., 2018a, 2018b). To find the pressure balance position, it needs to calculate the pressure files of tubing and annulus after annular pressure and liquid level are stable.

Hydrostatics Two Fluids in UShaped Tube YouTube
Digital density measurement using the oscillating U-tube principle The example of a tuning fork shows that by applying a mechanical impulse one can generate a sound with a characteristic pitch. This sound is the result of the oscillation created by deflecting the prongs of the tuning fork.
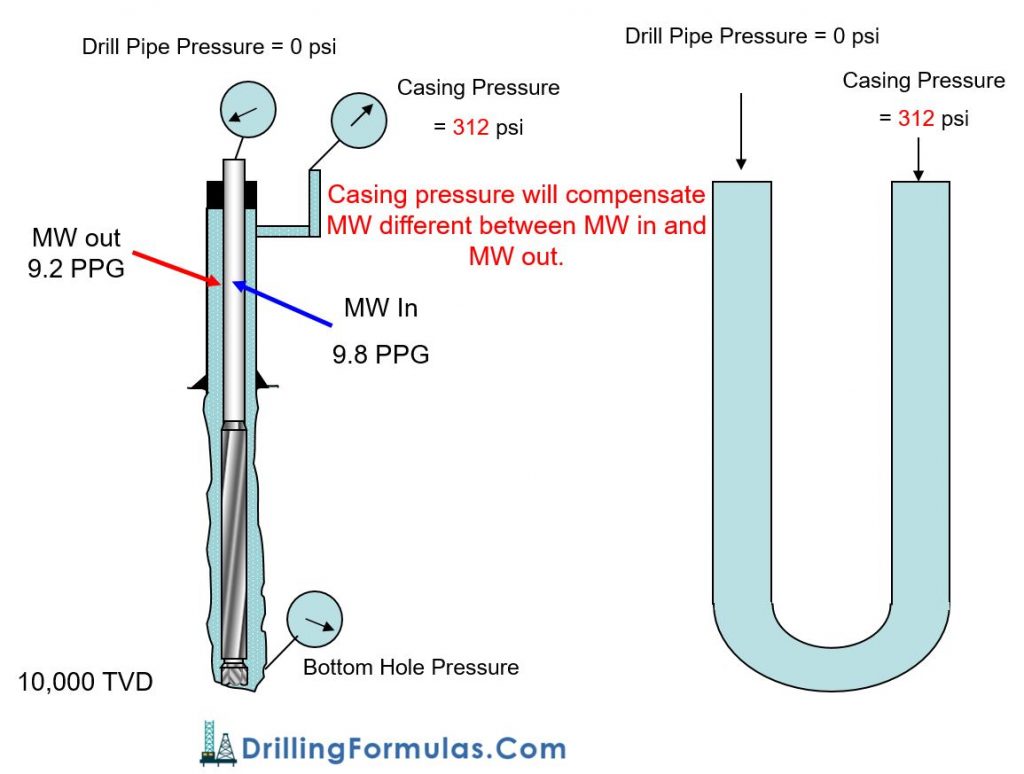
Understand UTube Concept and Importance of UTube
1) U-tube manometer Let's look at a U-tube manometer as it is probably the most common manometer in use today. We'll discuss how it is used to measure pressure. Types of fluids As we said earlier, a manometer is filled with a liquid. Typical manometer liquids are mercury, water, and light oils.

Let’s apply UTube concept Drilling Formulas and Drilling Calculations
Updated Jan. 5, 2024, 3:30 AM UTC. By NBC News. A 17-year-old student at Perry High School in Iowa fatally shot a sixth grader and wounded four other students and a school administrator Thursday.

Understand UTube Concept and Importance of UTube
The U-tube manometer principle is that when we apply pressure to be measured to one side of the tube produces a movement of liquid. The U-tube manometer has a U-shaped glass tube and a measuring scale. A manometer is an instrument that measures the gauge pressure.

Types of Manometers, Definition and Working Principle
It consists of a glass tube bent like the letter 'U'. In this type of manometer, balancing a column of liquid is done by another column of same or other liquid. One end of the U-tube is attached to the point where pressure is to be measured, while the other end is open to atmospheric pressure.
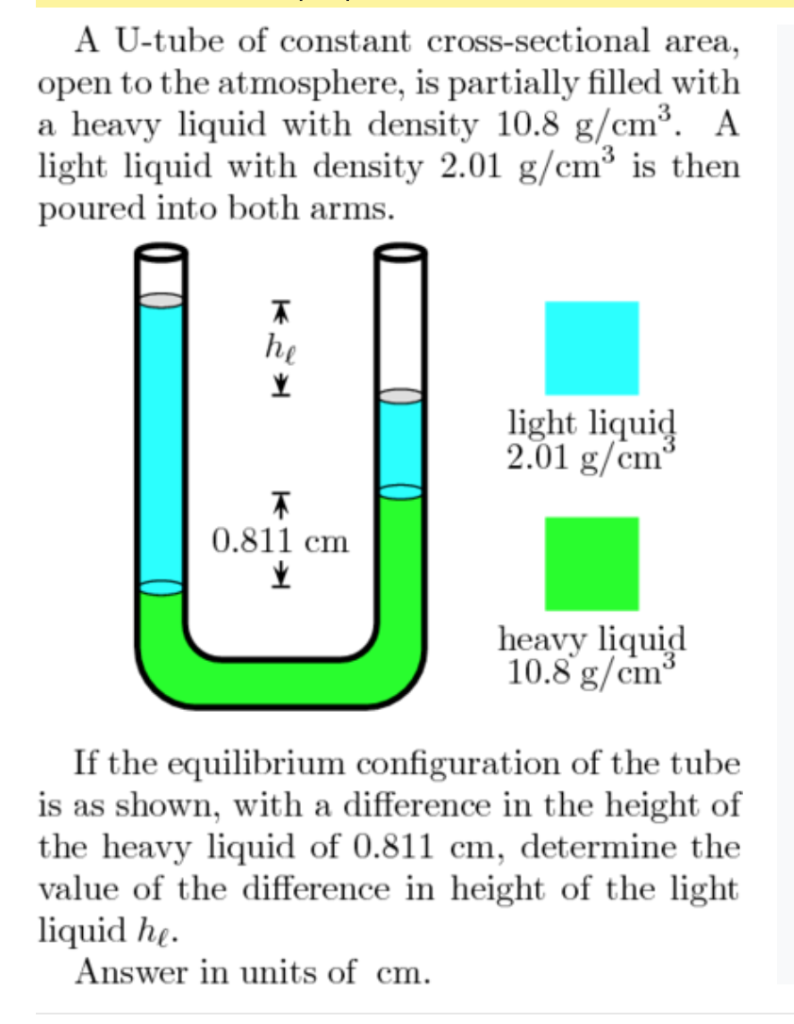
Solved A Utube of constant crosssectional area open to the
1. Overview-table: Density measurement techniques 2. What is density? 2.1. Density definition 2.2. What affects density? 2.3. Anomaly of water 2.4. Density units 3. Density measurement 3.1. History 3.2. Overview of density measurement techniques 3.2. In-depth: Measuring density with a digital density meter 3.2. Parts of a digital density meter 4.

Schematic diagram of the Utube principle. Download Scientific Diagram
U-Tube Principle drillingformulas 5.05K subscribers Subscribe 35 1.2K views 2 years ago U-Tube is a method to describing behavior of two fluid columns which are connected at the bottom. In.

Understand UTube Concept and Importance of UTube
The applied Pressure = ρ × g × h y suitable choice of filling liquid, various low ranges of gauge pressure can be measured from about 500 Pa to 1.5 bar. Typical filling liquids commonly used in manometers and their densities. Water ( ρ = 1000 kg m -3 ) Oil ( ρ can be between 800 and 950 kg m -3 ) Mercury ( ρ = 13560 kg m -3 ) Credits : N Asyiddin

PPT Introduction to Biology BELLWORK PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5353979
A built-in density measurement based on the oscillating U-tube principle allows the determination of kinematic viscosity from the measured dynamic viscosity employing the relation: The Stabinger Viscometer was presented for the first time by Anton Paar GmbH at the ACHEMA in the year 2000. The measuring principle is named after its inventor Dr.

Eğitimciler Bernoulli prensibi üzerinde mi çalışıyorlar?
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
Utube.html 06_04Utube.jpg
The oscillating U-tube is a technique to determine the density of liquids and gases based on an electronic measurement of the frequency of oscillation, from which the density value is calculated. This measuring principle is based on the Mass-Spring Model. Overfilling the oscillator beyond the bearing points is irrelevant to the measurement. For this reason the oscillator can also be employed.
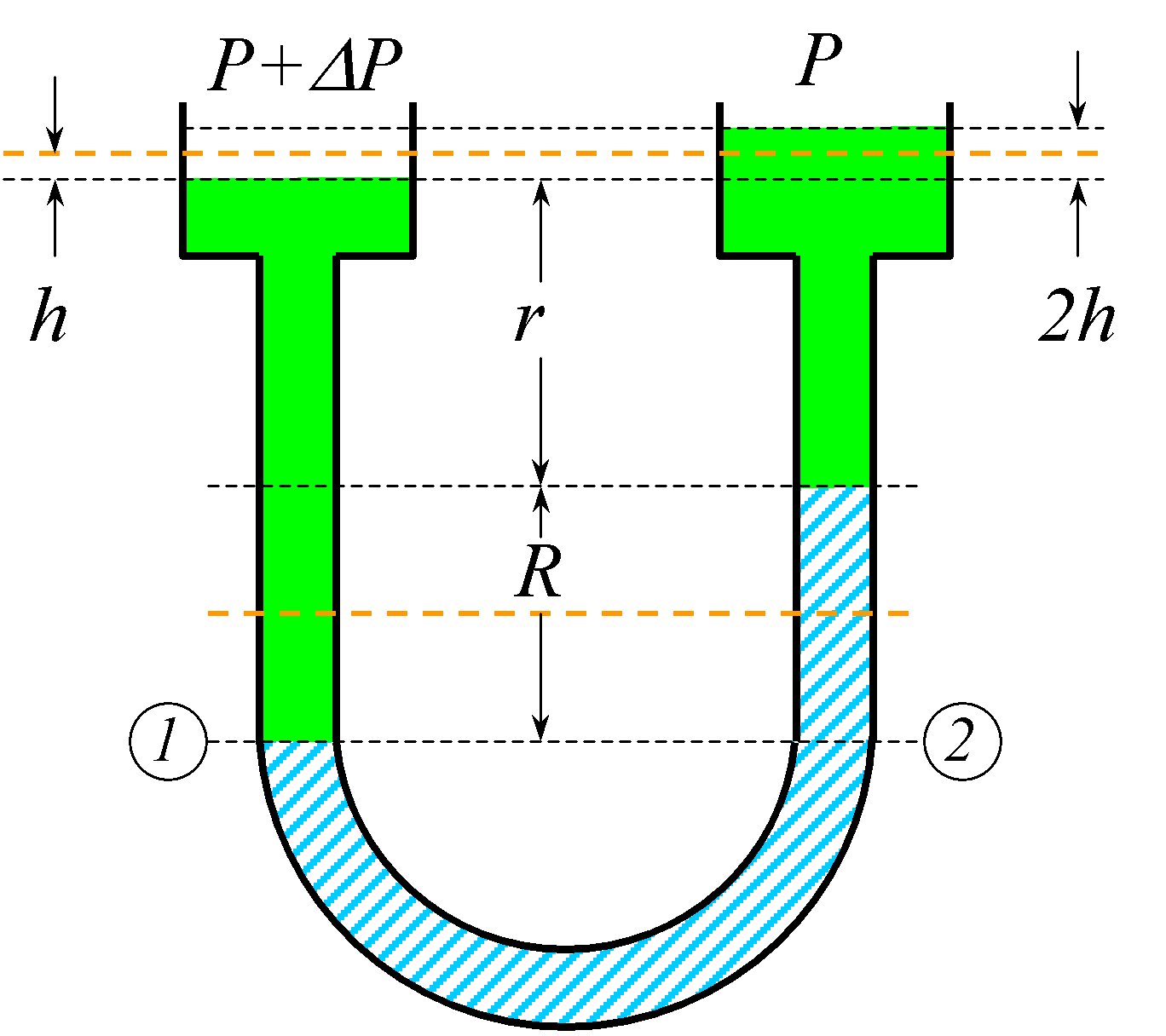
Instrumentation U Tube Manomerter Theory, Explanation, Diagram, & Working Equations
U-tube manometer working principle If the pressure from the additional gas/liquid supply is greater than the atmospheric pressure this will exert a downward pressure on the measuring liquid. As a consequence, the liquid will be pushed down on one side with the greater pressure causing the liquid to rise on the side with the lesser pressure.

UTube Manometer
Pressure range, sensitivity, dynamic response and cost all vary by several orders of magnitude from one instrument design to the next. The oldest type is the liquid column (a vertical tube filled with mercury) manometer invented by Evangelista Torricelli in 1643. The U-Tube was invented by Christiaan Huygens in 1661.

UTube Principle YouTube
This calculator can be used to calculate the differential pressure measured with an U-tube manometer. γ - of the fluid in the tube (kN/m , lb/ft (9.8 kN/m , 62.4 lb/ft default values for water) h - length of the liquid column along the tube (mm, ft) θ - angle of column relative the horizontal plane (degrees)

U Tube Manometer Instrumentation Systems YouTube
The oscillating U-tube is a technique to determine the density of liquids and gases based on an electronic measurement of the frequency of oscillation, from which the density value is calculated. This measuring principle is based on the Mass-Spring Model. The sample is filled into a container with oscillation capacity.